Table of Contents
What comes handy for you to reach the place you don’t know? Exactly, we are talking about maps and the driverless cars. Are you aware of the technology behind this whole exciting invention? No matter yes or no! You can get along if you are interested in LiDAR technology which has made driverless cars possible today or if you are considering to build up your ideas.
It is helping map applications and self-driving cars to work with a 3D map making technology. Here we will discuss what is LiDAR, the working principles, types and how this technology can work for various verticals.
Let’s get to it!
What is LiDAR?
LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging. It is similar to RADAR but uses light pulses instead of radio waves. Here we go with the definition of LiDAR.
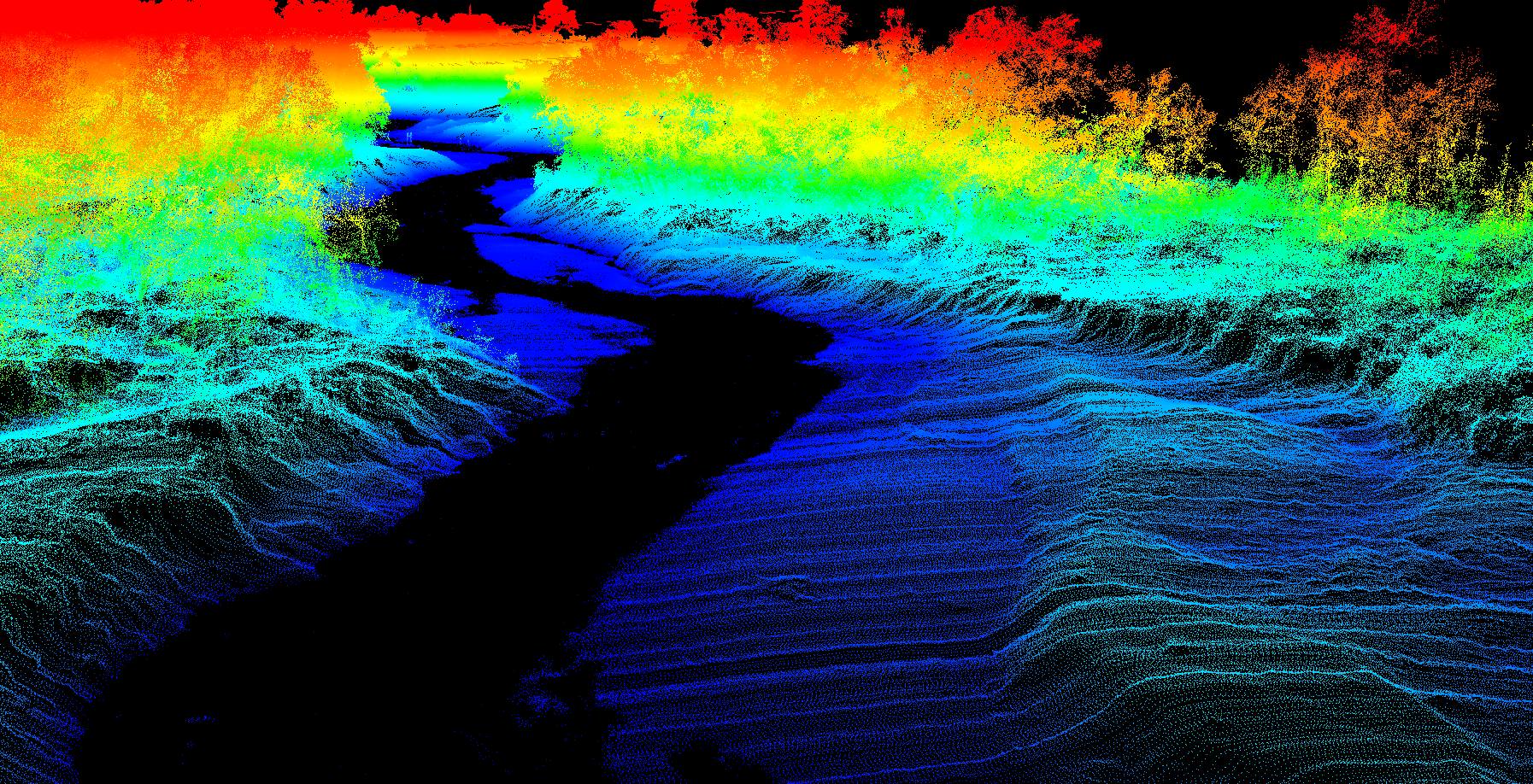
Lidar is a surveying method that measures the distance to a target by illuminating the target with laser light and measuring the reflected light with a sensor.
How does LiDAR work?
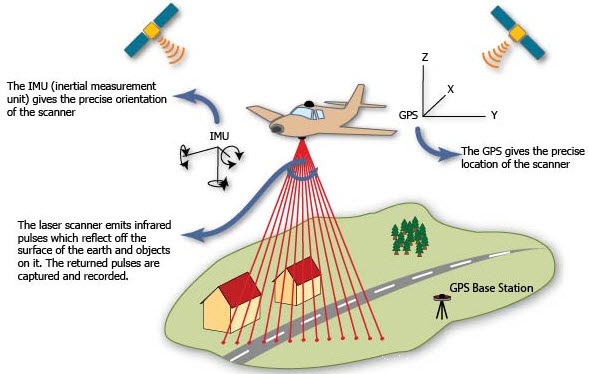
The working principle of LiDAR is quite simple. The LiDAR uses its sensor to transmit light pulses at any object on the earth’s surface to measure the time taken for each light pulse to rebound to the sensor. By means of this, the actual distance of the object can be calculated by,
Distance = (Speed of Light x Time of Flight) / 2
We know that Light travels at a constant speed so that the LiDAR technology can dramatically calculate the distance between its sensor and the object with high accuracy. By repeating this process and calculating accurate distances between each pulse, the elevation can be determined from the ground surface and from the various features such as building and vegetation.
Types of LiDAR
Today many sectors use LiDAR for various purposes for its improved technology and effective accuracy rates. let’s take a look at the types of LiDAR.
LiDAR has mainly four modes of collection.
1. Airborne LiDAR (ALS)
It uses an aircraft-mounted with a laser scanner to produce a point cloud. It is especially used to cover very large areas.
2. Terrestrial LiDAR (TLS)
This generally uses a tripod which is a stationary LiDAR sensor. It is used for close-range and high-accuracy applications.
3. Mobile LiDAR (MLS)
In MLS, a moving vehicle usually car mounted with a laser scanner is used. MLS are used in linear paths especially in roadways.
4. UAV/Drone
Drones are used in UAV Lidar to collect the Lidar point cloud. UAV LiDAR used for large areas and is cost-efficient.
In LiDAR scanning, an integrated GNSS/IMU (Global Navigation Satellite System/Inertial Motion Unit) is generally used in all modes of collection other than TLS to provide details about the position, rotation, and motion of the scanning platform.
Georeferencing in TLS is simply an identification of the position and orientation of the static scanner with the help of GCPs (Ground Control Points). But in MLS, ALS or Drones, the GNSS/IMU data should be adjoined with GCPs for georeferencing. This can be done in the post-processing work or during the flying simultaneously.
Usage of LiDAR technology in Industries
Forestry management
LiDAR can be used to generate Digital Elevation Models(DEM), Digital Surface Models(DSM) to measure the canopy surface and its density, to estimate the volume of surface and to understand the forest structures based on field measurements. They are further used for managing and planning in forest development.
Autonomous vehicles
Autonomous vehicles are the new technology the world is looking forward to. Lidar sensors provide highly accurate data for advanced driver assistance for a safe experience. In addition to Radar-based sensors, Lidar helps in identifying traffic signs and road markings, handling the speed control and steering control and also in viewing the objects in the surroundings with its continuous 360 degrees of visibility.
Agriculture
LiDAR can be used in developing a 3D elevation map of particular farmland, determining soil type, yield forecasting, and preventing soil erosion by generating contour. This 3D model can be further used to identify the water catchment area and the flow of erosion to advise farmers for the best practice to do.
Transportation
LiDAR is used to measure and understand the elevation and width of road pavement, railway tracks, airport runway and planning the transportation. By classifying the other features present near the pavements like culvert, bridges, powerlines and terminal buildings. MLS is used for the clear perspective and ALS used for the wide and faster coverage.
Military/Government
The usage of LiDAR has also improvised in the military for its high-quality accuracy in handling operations. Lidar is used for various purposes like surveillance, target identification and neutralization, mine detection, autonomous vehicles and generating 3d model of battle terrain
Furthermore, LiDAR technology is also used in the applications for 3D city modeling, Oceanography, Archaeology, River Survey, Meteorology, Mining, and various business sectors
Key Takeaways
LiDAR technology has the ability to generate Digital Elevation Models(DEM), Digital Surface Models(DSM), and Orthophoto, and Collecting point cloud. With the enhanced advances of Lidar systems and their associated data processing techniques helps in cost reduction and improved time processing.
The usage of these different types of lidar systems varies according to the needs of accuracy, efficiency, area coverage and the key applications of the sector. TLS is widely used in forestry management while ALS and MLS are used in transportation for rendering detailed road information.
For the ongoing advancement of these fields in the means of cost, range, and resolution, Lidar is a significant technology is a revolution in various aspects of mapping and 3D technologies.
RELATED POSTS
- Image Classification Techniques in Remote Sensing
- Top 10 Topographic Maps From Around the World
- Geographical Information System (GIS) in Urban Planning
Looking for more? Subscribe to weekly newsletters that can help your stay updated on Geographic Information Systems and Application developments.